Information Processes - The Seven
Information Processes
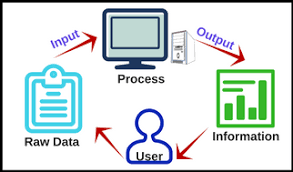
Information processes are what needs to be done to transform the data into useful information. These actions coordinate the system’s resources to achieve the system’s purpose. The information processes use the resources of the information system to process data into information in order to achieve the system’s purpose.
There are 7 important information processes in Unit 2. which are:
- Collecting
- Organising
- Analysing
- Storing & Retrieving
- Processing
- Transmitting & Receiving
- Displaying